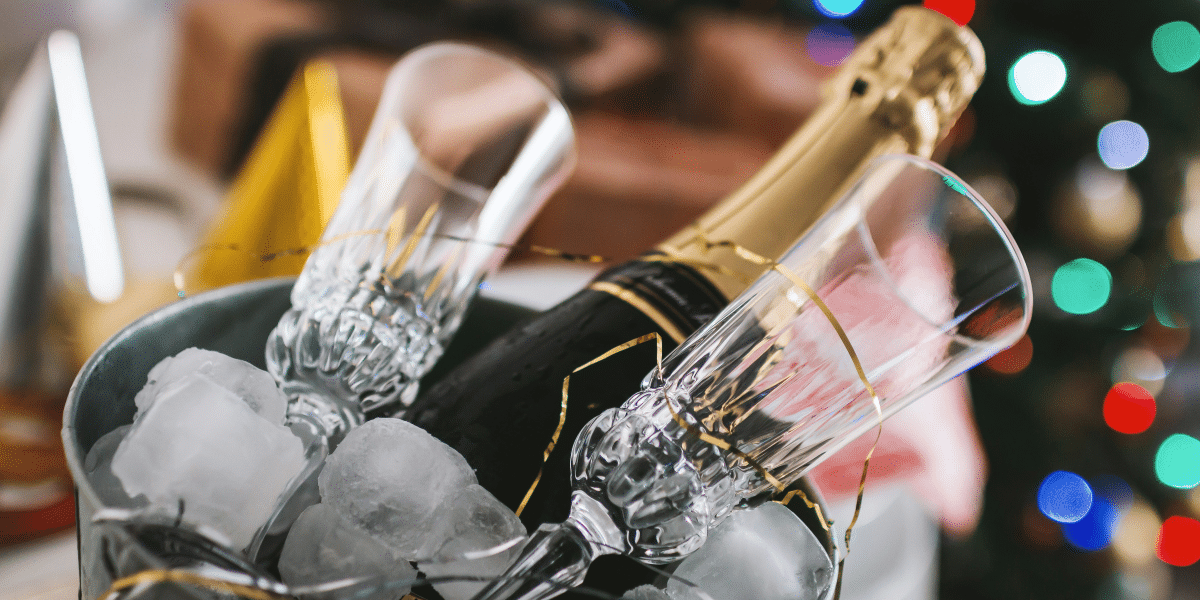8 Essential Tips for Hosting a NYE Party at Your House
New Year’s Eve parties are known for being memorable events that inspire a sense of anticipation for all that the future holds. While you already have an easy reason to invite your family and friends to celebrate the occasion, you might be wondering how to keep everyone happy and entertained as the clock makes its way toward midnight. Following these eight essential tips can help make hosting a memorable NYE party simple.
Open Up Time for Socializing With Catering Services
If there’s one mistake to avoid, it’s being stuck in the kitchen all night. Planning for catering services may eliminate one big worry from your to-do list. On top of having help with food prep, you might also find that using the catering menu to select appetizers, entrees, and beverages is a good way to keep everyone satisfied while you also get to enjoy the night.
Decide Upon a Dress Code
As the host, you have full control over the overall tone of the party. If you prefer a more formal celebration, then ask your guests to wear cocktail attire. Alternatively, you could send signals that the vibe might lean toward being more casual by letting everyone know to dress comfortably for a long night of fun ahead.
Create a Signature Cocktail
Serving drinks can be a fun way to get everyone to loosen up and have fun at your party. Champagne toasts are a tradition on New Year’s Eve, and you might enhance the ones at your party with a sprinkle of edible glitter. Or, you could consider getting extra fancy and concocting your own signature cocktail that could become the talk of the season.
Plan a Few Activities
Sure, the countdown is a big focus at NYE parties, but there’s lots of time to fill before the big ball drops. Depending upon your party crowd’s interests, you might explore options such as setting out some tabletop games. Or, you could host a murder mystery party. A crafty group may enjoy making vision boards for the new year.
Set the Scene With Festive Decorations
If you love sparkles, then this is your time to shine. Most people choose glittery, metallic colors for NYE parties. Adding touches of festive garland and centerpieces to the party room can help get everyone in the mood for fun. If you plan to host more NYE parties in the future, then you might want to pick out timeless decorations that you can use year after year while mixing in a few that highlight the specific date.
Arrange to View the Ball Drop
Many people make watching the ball drop part of their annual NYE tradition. Make sure to have a viewing area somewhere in the main party space where people can enjoy the performances and wait for the big moment. Using a projector might provide everyone with a way to view the ball drop from wherever they are in the room.
Make Detailed Invitations
People may be more likely to accept your invitation when they know what to expect. Once you have your plans, make sure to add the little details that help answer their questions. For instance, you could note that the party is kid-friendly if you are inviting families. Or, you might want to let everyone know that there’s an after-party so that people can arrange to stay later.
Help People Get Home Safely
Responsible hosting means ensuring that every guest leaves your party safely. If you know people who plan to drink, then keep an eye out to make sure that they have a designated driver. This is also a great time to make sure you have info for local transportation services such as taxis for anyone who needs assistance.
Starting early is often a helpful way to ensure that you have time to put all of your plans into action. Arranging for food services, picking out decorations, and sending invitations can help you feel confident that you have everything in place long before the party starts. By being proactive, you’ll be ready to enjoy a potentially stress-free NYE that may start your new year off right.
Published by Mark V.